The Eclipse Development Environment is easily configured to use the Alta distribution shared object files.
Here’s an example of how we did it:
1) Create your C or C++ project in Eclipse using the Linux GCC toolchain. For this discussion, we will use project named ADT_L1_Test.
2) Import the following files into you project workspace (workspace/ADT_L1_Test) using the import->file system Eclipse tab.
ADT_L0.h
ADT_L1.h
libADT_L0_Linux_x86_64.so (or libADT_L0_Linux_x86_32.so for 32 bit Linux)
libADT_L1_Linux_x86_64.so (or libADT_L1_Linux_x86_32.so for 32 bit Linux)
ADT_L1_1553_ex_rt1.c (or other Alta example source, or your own main source)
3) Verify that your project now looks something like:

4) Modify the Project Properties by right-clicking on the Project name (ADT_L1_Test) and choosing Properties. Add the shared object filenames, without the leading lib and trailing .so extensions, as well as the library path to your workspace.
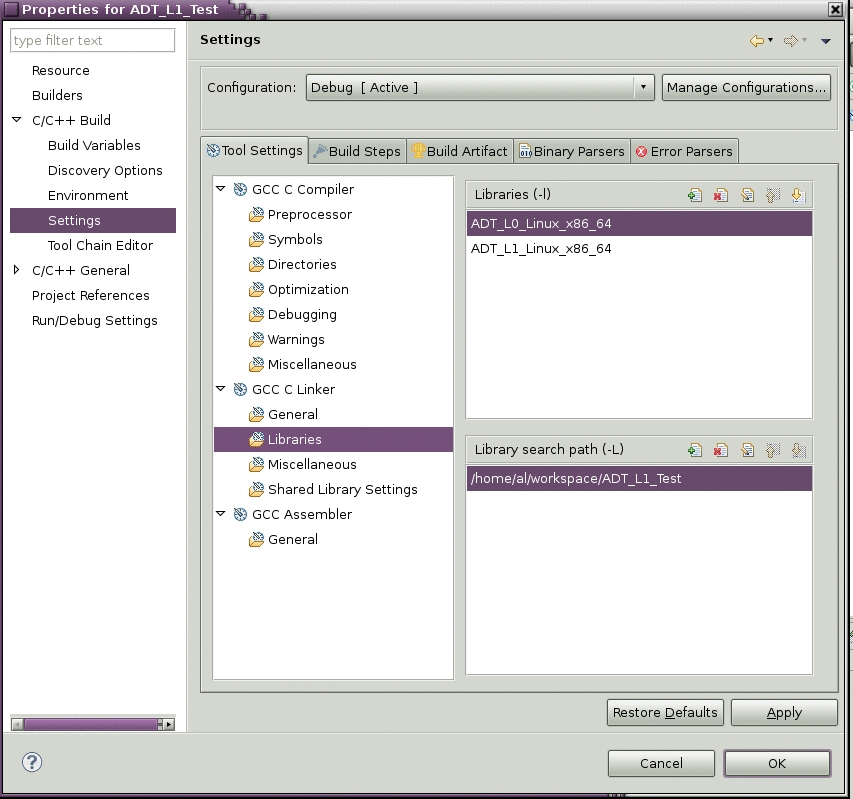
5) Copy the shared object files to either or both target directories, Debug and/or Release.
6) Build and run your program!

